Which Structure Provides A Protective Outer Covering For Bones And Assists With Fracture Repair?
Molar Anatomy - Tissues of a Molar
The Anatomy of a Tooth
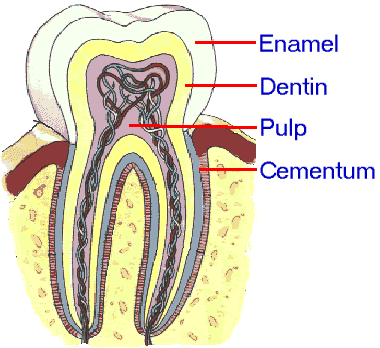 Although humans take 4 different types of teeth with pregnant variations in their external morphology, they all share a common internal dental beefcake. All human teeth consist of 3 main layers. The external and hardest of all layers is the enamel, underneath of enamel there is dentin, and at the middle of the molar lies the softer and live role of the tooth, the pulp.
Although humans take 4 different types of teeth with pregnant variations in their external morphology, they all share a common internal dental beefcake. All human teeth consist of 3 main layers. The external and hardest of all layers is the enamel, underneath of enamel there is dentin, and at the middle of the molar lies the softer and live role of the tooth, the pulp.
A basic noesis of the internal anatomy of the tooth and its structure is necessary in order to sympathise the evolution of several dental weather condition, their causes and their treatments. If nosotros take a section of a human being tooth we will be able to distinguish 4 unlike types of tissues, enamel, cementum, dentin, and pulp tissue. The main characteristics of each part of the tooth structure are described in this article (for more than detailed data about each i follow the links to the specific pages).
The main parts of tooth beefcake are Enamel, Dentin, Cementum, and Pulp.
The Molar Enamel
Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth structure of the crown, the part of the tooth that is above the gums. Dental enamel is the hardest and most mineralized substance in the human being body. Information technology looks like bone just it is much harder, denser, and its composition is 96% inorganic.
Dental enamel offers a protective cover to the entire top of the tooth with its thickest bespeak at the cusps of the molar. Information technology becomes thinner at the edges of the tooth closer to the glue line, upwardly to the cement-enamel junction (CEJ) where it is substituted past the cementum that covers the root.
It is slightly translucent, so any modify in the color of the underlying dentin, either due to the development of tooth decay, or due to discoloration unremarkably becomes visible through the enamel. Its natural color can vary from grayish white to yellowish.
Although dental enamel is the hardest tissue of the homo body, information technology is very vulnerable. Due to its very dense mineral structure, it is highly susceptible to acidic impairment (demineralization), the master cause of tooth decay. Enamel is also very brittle, specially when not supported by sound underlying dentin. The chief disadvantage of dental enamel is that it lacks the ability of repairing itself, as bones have. Whatever structural damage to the tooth enamel is permanent and can't be repaired naturally by our trunk.
The Cementum
Cementum is the outer layer of the molar structure for the root part of the tooth which lies nether the gum line. It is a bonelike fabric, almost as hard as enamel, simply with a less inorganic limerick. Cementum is light xanthous in colour, slightly lighter than dentin. Information technology is non translucent as the enamel.
The main part of cementum is to protect the roots and anchor the teeth in their sockets inside the jaw bone. A network of fibers made of connective tissue (known as periodontal ligament) connects the cementum with the alveolar bone and go along the tooth steady in its socket (for more details encounter ΄periodontium΄).
Information technology is more than susceptible than enamel to molar disuse, peculiarly due to the college aggregating of bacterial plaque and dental calculus forth the gum line, or underneath it (sub-gingival plaque). Unlike enamel, cementum is formed continuously throughout the life of the tooth to compensate for the substance loss due to tooth vesture, and to let for the attachment of new fibers of the periodontal ligament to the surface of the root.
The Dentin
Dentin is a bone-similar material that makes upwardly most of the molar's construction. Information technology is covered past the enamel in the crown and past the cementum in the root area of the tooth. It engulfs and protects the living part of the tooth, the pulp tissue.
Dentin has a lite yellow colour, which gives the tooth its natural colour prevailing through the almost translucent enamel. Information technology consists of seventy% inorganic materials, with a spongy, porous structure fabricated of tubules extending from the enamel to the pulp chamber. Nerve endings enter the dentinal tubules and may transmit signals such as pain in response to external stimuli.
Dentin is harder than bone but softer than enamel. It becomes very vulnerable to molar decay if the protective cover of enamel or cementum is lost or weakened. However, the dentin is a living tissue, so it has the power for some degree of growth and repair in response to certain physiologic and pathologic conditions.
The Dental Pulp
The dental lurid is the soft living tissue of the tooth. It can be found in the pulp chamber, a cavity in the heart of the crown of each molar, and inside the root canals which connect the pulp crenel with the opening at the root tip (apex) and through that with the rest of the body. The pulp contains blood vessels, connective tissue, nerves, and other cells including odontoblasts, fibroblasts, macrophages and lymphocytes.
The master part of the pulp is providing awareness and nourishment to the molar, and the formation of dentin and cementum. The pulp tissue responds to irritation either by forming reparative secondary dentin for protection confronting the source of irritation or by becoming inflamed.
The pulp, every bit the living part of the molar, has a high risk of infections. If bacteria manage to accomplish the pulp, east.grand. due to molar decay or through a crack of the molar, they cause inflammation which is usually very painful due to the high pressure that is developed within the enclosed space of the pulp chamber. If the pulp is infected and a dental abscess has developed, a root canal therapy is necessary to prevent further impairment.
![]()
next page -> Teeth Names & Numbers
Source: https://www.mouthandteeth.com/anatomy/tooth-anatomy.htm
Posted by: harrisdreatenty.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Structure Provides A Protective Outer Covering For Bones And Assists With Fracture Repair?"
Post a Comment